Featured Snippet Summary
Search Engine Optimization is the process of improving a website so it appears higher on search engines like Google. It works by creating helpful content, using the right keywords, improving website structure, and earning trusted backlinks. When done correctly, SEO helps people find your website faster and increases traffic without paying for ads.
Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 What Is Search Engine Optimization?
- 3 Why Search Engine Optimization Matters
- 4 How Search Engines Work (Simple Explanation)
- 5 The Main Goals of Search Engine Optimization
- 6 Core Elements of SEO
- 7 Why Search Engine Optimization Is a Long-Term Strategy
- 8 User Intent: The Heart of Search Engine Optimization
- 9 Examples: Simple Explanation of SEO in Action
- 10 Deep Dive Into How Search Engine Optimization Works (On-Page, Off-Page, Technical, Content SEO with Examples)
- 11 On-Page SEO: Improving What Happens on Your Website
- 12 Off-Page SEO: Building Trust and Reputation Outside Your Website
- 13 Technical SEO: Making Your Website Fast, Clean, and Search-Friendly
- 14 Content SEO: Creating Useful Information That Matches the User’s Intent
- 15 Bringing All SEO Elements Together
- 16 SEO Examples for Businesses
- 17 Common SEO Mistakes
- 18 How Beginners Can Start SEO
- 19 The Future of SEO with AI
- 20 25 SEO FAQs
- 21 Conclusion
Introduction
Search engines are a major part of everyday life. Whenever someone wants to learn something, compare products, or buy online, the first place they go is Google. But with millions of websites online, only a few reach the top results. The reason is simple: these websites use Search Engine Optimization.
This article gives a clear, simple explanation of what Search Engine Optimization is, why it matters, and how it works. Everything is explained in a way that even a 5th-grade student can understand, while keeping the tone professional and based on real SEO principles.
What Is Search Engine Optimization?
Search Engine Optimization is the process of improving your website so search engines can understand it easily and rank it higher. When a page ranks higher, more people see it, click it, and trust it. SEO helps a website appear in front of the right audience at the right time.
The idea behind Search Engine Optimization is simple:
Make your website useful, clear, fast, and trustworthy. When a site meets these conditions, search engines reward it with higher visibility.

Why Search Engine Optimization Matters
Search Engine Optimization is important because most people never scroll past the first page of Google. When your website appears on top results:
• More people find your business
• You get visitors without paying for ads
• Your brand becomes more trusted
• You get more leads, sales, and traffic
• You stay ahead of competitors
SEO is one of the few marketing strategies that continues to work for years. A single well-optimized page can bring traffic every day without any extra cost.
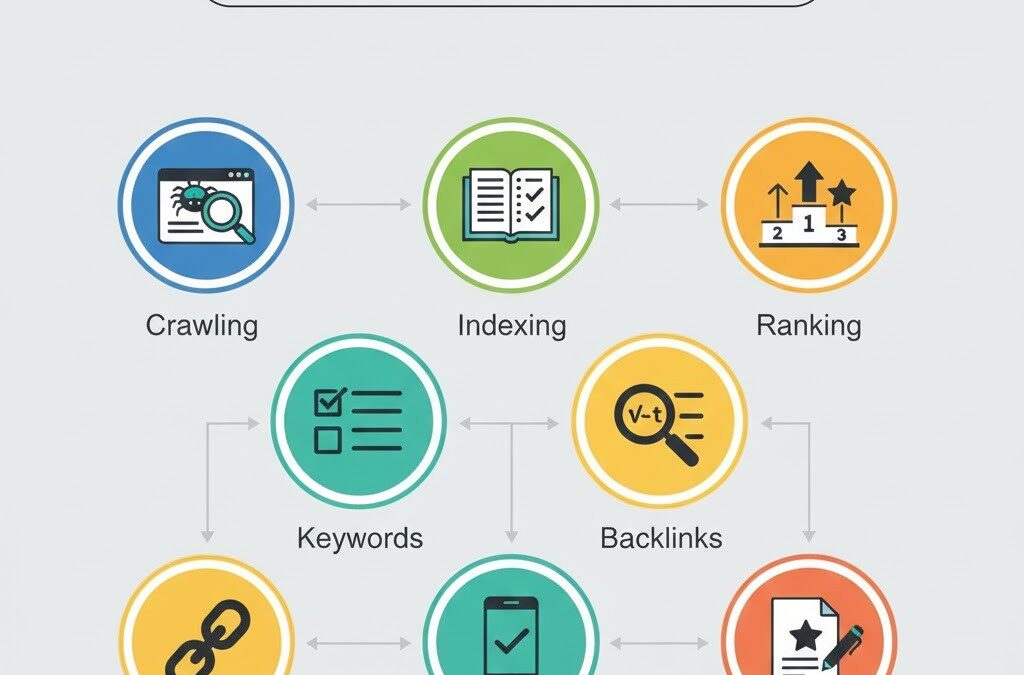
How Search Engines Work (Simple Explanation)
Search engines follow a basic 3-step process:
1. Crawling
Search engines send small programs called crawlers to visit web pages and discover new content.
2. Indexing
Once crawled, the page is stored in Google’s index. This allows Google to understand what the page is about.
3. Ranking
When a user types a query, Google ranks pages based on relevance, usefulness, and quality.
Search engines use hundreds of factors to decide ranking. The goal is to provide the most helpful content to users.
The Main Goals of Search Engine Optimization
Good Search Engine Optimization focuses on four goals:
1. Make the website easy to understand
Your content should clearly explain what your page is about.
2. Improve user experience
Pages should load fast, be mobile-friendly, and simple to navigate.
3. Provide helpful content
Google rewards websites that answer user questions in a clear and complete way.
Search engines trust websites that have high-quality backlinks from other respected sites.
Core Elements of SEO
Search Engine Optimization is made up of several important elements. Each plays a role in helping your site rank higher.
1. On-Page SEO
Improving things directly on your website, like:
• Keywords
• Headings
• Content quality
• Meta tags
• Internal links
2. Off-Page SEO
Improving your website’s reputation outside your site through:
• Backlinks
• Brand mentions
• Social signals
• Online reviews
3. Technical SEO
Making your website technically strong, including:
• Fast loading speed
• Mobile-friendly design
• Secure connection (HTTPS)
• XML sitemaps
• Structured data
4. Content SEO
Creating helpful, clear, high-quality content based on user intent.
Good SEO requires all four working together. If one area is weak, overall rankings fall.
Why Search Engine Optimization Is a Long-Term Strategy
SEO is not a one-day or one-week project. Search engines take time to evaluate a website. Rankings grow slowly but steadily. Once a page gains authority, it stays visible for a long period.
Unlike paid ads, which stop when you stop paying, SEO continues to work. This makes Search Engine Optimization one of the best long-term investments for businesses.
User Intent: The Heart of Search Engine Optimization
User intent means understanding what people are searching for. Search engines want to provide the best possible answer for every query. Search Engine Optimization focuses on matching your content to the user’s needs.
There are four types of intent:
- Informational: user wants to learn
- Navigational: user wants a specific site
- Commercial: user wants to compare
- Transactional: user wants to buy
When your content aligns with the right intent, search engines boost your ranking.
Examples: Simple Explanation of SEO in Action
Here are a few examples of how Search Engine Optimization works in real life:
Example 1: A bakery website
If a bakery wants to rank for “fresh cakes near me,” SEO helps them create:
• a page explaining their cakes,
• fast-loading photos,
• correct keywords,
• and Google Maps listing.
Example 2: A clothing store
A fashion shop can rank for “casual shirts for women” by:
• writing a helpful product page,
• adding high-quality images,
• using descriptive titles,
• and building social proof.
Example 3: A blog
A blog can appear at the top results by answering questions clearly and providing detailed content on the topic.
These examples show that Search Engine Optimization applies to all industries.
Deep Dive Into How Search Engine Optimization Works (On-Page, Off-Page, Technical, Content SEO with Examples)
Search Engine Optimization becomes powerful when all its components work together. In this section, we explore each major type of SEO in detail, how they influence ranking, and how you can use them to grow your website step by step.
This part focuses on practical, real-world explanations rather than technical jargon. The goal is to help you clearly understand how to apply Search Engine Optimization simply and effectively.
On-Page SEO: Improving What Happens on Your Website
On-page SEO refers to everything you control directly on your website. If search engines cannot understand your page, they cannot rank it. That is why on-page optimization is often the first step in Search Engine Optimization.
1. Using the Right Keywords (Primary + LSI Keywords)
Keywords help search engines understand what your page is about.
There are two main types:
Primary Keyword
This is the main term you want to rank for.
Example: Search Engine Optimization
LSI Keywords (Related Terms)
These are supporting phrases that help search engines get more context.
Examples:
• SEO techniques
• how SEO works
• search ranking
• website optimization methods
Using these naturally in your content helps improve ranking and relevance.
2. Writing Clear and Helpful Headlines
Search engines read your headings (H1, H2, H3) to understand the structure of your content.
Good headings:
• Explain what each section covers
• Are simple and descriptive
• Match the user’s search intent
Example of a strong heading:
“How Search Engine Optimization Improves Website Visibility”
This clearly tells search engines and readers what to expect.
3. Optimizing Meta Titles and Descriptions
These appear in search results. They influence click-through rate (CTR).
A good meta title:
• Includes the main keyword
• Is short and clear
• Matches the user’s intent
A strong meta description:
• Summarizes the page
• Encourages clicks
• Uses natural language
Search Engine Optimization improves when your metadata is compelling and relevant.
4. Internal Linking (Connecting Your Pages)
Internal links help users navigate your site easily.
They also help search engines:
• Discover more pages
• Understand topic importance
• Spread authority across your website
Example:
A blog about “SEO basics” should internally link to pages like:
• Keyword research
• Technical SEO
• Link building guide
This builds topical authority.
5. Adding Helpful Images and Alt Text
Search engines cannot “see” images, so alt text helps them understand image content.
Example alt text:
“Search Engine Optimization process flowchart showing crawling, indexing, and ranking.”
This improves image search ranking and accessibility.
Off-Page SEO: Building Trust and Reputation Outside Your Website
While on-page SEO focuses on your website, off-page SEO strengthens your site’s authority. Search engines look for signals that other people trust your content.
1. Backlinks (The Most Important Off-Page Factor)
A backlink is a link from another website to yours.
Search engines treat backlinks like votes.
More high-quality votes = higher ranking.
Not all backlinks are equal.
Strong backlinks come from:
• Trusted websites
• Relevant industries
• High-authority blogs
• News publications
Weak or spammy backlinks can harm your ranking.
2. Brand Mentions (Even Without Links)
Search engines now track brand mentions.
If people online talk about your brand, Google sees it as a trust signal.
Examples:
• Social media comments
• Industry discussions
• Blogs mentioning your brand name
The more your brand appears, the stronger your authority.
3. Reviews and Ratings
Google uses customer reviews to measure trust.
More positive reviews help businesses rank better in:
• Local search
• Google Maps
• Niche searches
Example:
A restaurant with 4.9 stars and 1,000 reviews will outrank a restaurant with 3.5 stars and 40 reviews.
4. Social Signals
Likes, shares, comments, and engagement also influence visibility.
While not a direct ranking factor, social signals help your content reach more people.
Technical SEO: Making Your Website Fast, Clean, and Search-Friendly
Technical SEO ensures that search engines can crawl and index your website without difficulty. Even great content cannot rank if your site has technical issues.
1. Website Speed
Slow websites lose rankings because users leave when pages take too long to load.
To improve speed:
• Compress images
• Use a fast hosting provider
• Remove unnecessary code
• Enable caching
Fast websites provide a better user experience, which increases engagement.
2. Mobile-Friendly Design
Most searches happen on mobile devices.
Search Engine Optimization improves when your site:
• Loads correctly on small screens
• Has readable fonts
• Buttons are easy to click
• Layout adjusts automatically
Google uses mobile-first indexing, meaning it ranks your site based on the mobile version.
3. Secure Connection (HTTPS)
Security is part of Google’s ranking system.
If your site uses HTTPS, users and search engines trust it more.
4. XML Sitemaps
A sitemap helps search engines find all your pages quickly.
It acts like a directory that guides crawlers.
5. Structured Data (Schema Markup)
Structured data helps Google understand your content deeply.
It can unlock features like:
• Rich snippets
• FAQ boxes
• Product ratings
• How-to steps
This improves visibility in both traditional and AI-powered search results.
Content SEO: Creating Useful Information That Matches the User’s Intent
Content is the heart of Search Engine Optimization.
If your content is strong, helpful, and complete, it has a higher chance of ranking well.
1. Matching User Intent
Every search has a purpose.
Your content must match that purpose.
Examples:
Search: “What is SEO?”
Intent: Learn the basics
Content needed: Simple explanation
Search: “Best SEO tools.”
Intent: Compare products
Content needed: Lists, reviews
Search: “SEO service near me.”
Intent: Buy
Content needed: Business page, contact info
2. Creating High-Quality, Helpful Content
High-quality content is:
• Clear
• Detailed
• Accurate
• Easy to read
• Useful to beginners
Good content straightforwardly answers questions without confusion.
3. Using Examples to Improve Understanding
Examples help people understand complex ideas easily.
Example:
“Search Engine Optimization is like placing a signboard on a crowded street. The clearer your sign, the more people notice your shop.”
Examples improve retention and engagement.
4. Avoiding Thin or Repetitive Content
Google does not reward pages that:
• Are too short
• Add no value
• Repeat the same information
Every page must offer something unique and helpful.
Bringing All SEO Elements Together
Here is a simple way to understand how Search Engine Optimization works when all parts are combined:
• On-page SEO tells Google what your page is about
• Off-page SEO shows Google that others trust you
• Technical SEO ensures Google can crawl and index your site
• Content SEO makes your page useful for real users
When these four work together, your website becomes stronger, more visible, and more authoritative
SEO Examples for Businesses
Example 1: Local Restaurant
A local restaurant can use SEO to appear in “restaurants near me” searches. By optimizing their Google Business Profile, including menus with keywords like “vegan pasta” or “Italian desserts,” and encouraging positive reviews, they attract more local customers.
Example 2: E-commerce Store
An online clothing store can rank for “summer dresses for women” by writing detailed product descriptions, using high-quality images with alt text, adding customer reviews, and building backlinks from fashion blogs.
Example 3: Service-Based Business
A plumbing service can rank for “emergency plumber in Dubai” by creating helpful content about common plumbing problems, adding location-based keywords, and optimizing their website for mobile users.
Example 4: Blog/Content Website
A blog about digital marketing can rank for “SEO tips for beginners” by creating long-form guides, including visuals, internal linking, and citing trustworthy sources.
Example 5: SaaS or Software
A software company can rank for “project management tools” by creating comparison pages, tutorials, case studies, and gathering backlinks from industry publications.
These examples show that SEO works for any type of business, big or small, online or offline.
Common SEO Mistakes
- Ignoring Mobile Users – Most searches are mobile-first. Websites not optimized for mobile lose traffic.
- Keyword Stuffing – Overusing keywords can hurt ranking and readability.
- Poor Website Speed – Slow-loading pages frustrate users and reduce rankings.
- Not Using Internal Links – Pages without internal links are harder for Google to index.
- Low-Quality Backlinks – Links from spammy sites can damage credibility.
- Thin Content – Pages with too little useful information fail to rank.
- Ignoring User Intent – Writing content that doesn’t answer what users want reduces clicks.
- Neglecting Meta Titles & Descriptions – This reduces click-through rates from search results.
- Duplicate Content – Copying content from other sites can cause penalties.
- Not Tracking Results – Without analytics, you cannot measure what works or improve strategy.
How Beginners Can Start SEO
- Start with Keyword Research – Use free tools like Google Keyword Planner or Ubersuggest to find terms people search for.
- Optimize One Page at a Time – Focus on writing high-quality, informative content for a single topic.
- Set Up Google Search Console – Track indexing, impressions, and clicks for your site.
- Improve Website Speed – Compress images, use a good hosting provider, and remove unnecessary plugins.
- Create Internal Links – Connect related content within your site to improve navigation and authority.
- Use Basic On-Page SEO – Include keywords in headings, meta tags, and alt text for images.
- Build Local Presence – For small businesses, claim Google My Business and encourage reviews.
- Learn From Competitors – Analyze top-ranking pages in your niche to see what works.
- Be Patient – SEO takes weeks or months to show results, so consistency matters.
- Keep Learning – Follow SEO blogs, updates, and algorithm changes to stay current.
The Future of SEO with AI
AI is reshaping SEO in several ways:
- AI-Powered Content Analysis – Tools like ChatGPT can suggest content improvements based on user intent.
- Voice Search Optimization – AI assistants like Alexa or Siri rely on concise, natural answers.
- AI-Generated Keywords – Predict trending keywords faster than manual research.
- Automated SEO Audits – AI can identify technical issues and suggest fixes quickly.
- Personalized Search Experiences – AI helps search engines provide hyper-relevant results for individual users.
SEO will increasingly combine traditional strategies with AI insights, making optimization smarter, faster, and more user-focused.
25 SEO FAQs
- What is SEO?
SEO is the process of optimizing a website to rank higher on search engines like Google. - Why is SEO important for businesses?
It increases organic traffic, brand visibility, and potential sales without paying for ads. - How long does it take for SEO to work?
Usually 3–6 months, depending on competition, website authority, and strategy. - What is on-page SEO?
Optimizing elements on your website like content, headings, meta tags, and internal links. - What is off-page SEO?
Activities outside your website, including backlinks, social mentions, and reviews. - What is technical SEO?
Optimizing website speed, mobile-friendliness, site structure, and security for search engines. - What are backlinks?
Links from other websites pointing to your site, acting as votes of trust for search engines. - What is keyword research?
Finding words and phrases people use to search for content or products online. - What is user intent in SEO?
Understanding what a user wants when they type a query, like learn, compare, or buy. - What are LSI keywords?
Related terms that provide context to your main keyword for better ranking. - Can SEO work for small businesses?
Yes, local SEO strategies can help small businesses attract nearby customers. - Does social media affect SEO?
Indirectly, social engagement can increase visibility and traffic, which may help rankings. - What is a meta description?
A summary of a page that appears in search results to encourage clicks. - What is a sitemap?
A file that lists all pages of a website to help search engines index them. - What is schema markup?
Structured data that helps search engines understand content better, like ratings or FAQs. - Is SEO free?
You don’t pay for clicks, but time, tools, and content creation cost money. - Can SEO bring fast results?
Organic SEO is slow by nature; paid ads are faster for immediate traffic. - How do I track SEO performance?
Using tools like Google Analytics, Search Console, or SEO software like SEMrush. - What is local SEO?
Optimizing your website to appear in location-based searches, like “plumber near me.” - What is thin content?
Pages with little or no useful information that search engines don’t value. - Do keywords still matter?
Yes, but relevance, intent, and context are more important than exact matches. - What is duplicate content?
Content that appears on multiple pages or websites can hurt rankings. - How often should I update my website for SEO?
Regularly, especially content updates, new posts, and technical improvements. - What is mobile-first indexing?
Google ranks sites based on the mobile version because most users search on mobile. - Is AI replacing SEO professionals?
AI assists in optimization, but human strategy, creativity, and quality oversight remain essential.
Conclusion
Search Engine Optimization is a critical skill for any business or website. By combining on-page, off-page, technical, and content SEO, you can improve visibility, attract the right audience, and grow your brand sustainably. Beginners should focus on high-quality content, user intent, and website usability while staying consistent over time.
For more in-depth guidance, explore our full SEO Guide for Beginners to learn advanced tips, tools, and strategies to take your website to the top of search results.